SNR is defined as the ratio of the output signal voltage level to the output noise level. It is usually represented in decibels (dB) and calculated using the following formula.
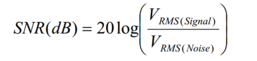
For example if the output signal amplitude is 1V(RMS) and the output noise amplitude is 1mV(RMS), then the SNR value would be 60dB. The above formula is a general definition for SNR. The SNR value of an ideal ADC is calculated using the following formula:
SNR (dB) = 6.02N+1.76(dB)
where N is the resolution (no. of bits) of the ADC. For example an ideal 10-bit ADC will have an SNR of approximately 62dB.
Note: In
practical applications,
to
achieve better
performance,
the SNR value of an ADC should be higher.