Whenever an input signal of a particular frequency passes through a non-linear device, additional content is added at the harmonics of the original frequency. For example, assume an input signal having frequency f. Then the harmonic frequencies are 2f, 3f, 4f, etc. So non-linearity in the converter will produce harmonics that were not present in the original signal. These harmonic frequencies usually distort the output which degrades the performance of the system. This effect can be measured using the term called total harmonic distortion (THD).
THD is defined as the ratio of the sum of powers of the harmonic frequency components to the power of the fundamental/original frequency component. In terms of RMS voltage, the THD is given by,
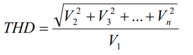
The THD value increases with the increase in the frequency. The THD should have minimum value for less distortion. As the input signal amplitude increases, the distortion also increases.