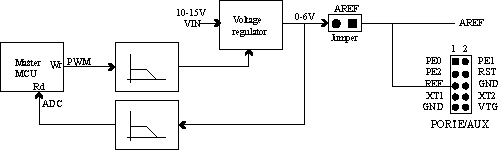
The Analog Reference voltage (AREF) can supply the reference voltage to the on-chip A/D converter on the Atmel AVR. If the AREF jumper is mounted, the on-board Analog Reference voltage is connected to the AVR’s AREF. The On-board Analog Reference voltage can be adjusted from Atmel Studio to 0 - 6.0V, but not above VTARGET.
When the AREF jumper is disconnected, AREF voltage must be supplied from an external source at the AREF pin on the PORTE/AUX header.
When using external an source for AREF, the user must control that VTARGET is at a higher voltage level than AREF. This can be controlled easily by reading the VTG value from Atmel Studio before setting AREF.
The Atmel STK500 master MCU controls the Analog Reference Voltage using the internal PWM. The AVR’s AREF signal is also accessible on the PORTE header; this pin can also be used for external AREF signal. The figure below shows the internal connection of the AREF signal.
The Atmel Studio controlled Analog Reference Voltage can also be used as an input to the analog comparator or for ADC measurements on the AVR. AVR’s AREF signal can then be connected to VTG.
The internal AREF has a short circuit protection. If an AREF value is set up to be higher than 0.3V and the Master MCU measures it to be below 0.3V for a duration of 80 ms, the master MCU will shut off the AREF. When this happens, the status LED will blink slowly.
The AREF will also be shut down by the Master MCU if a short circuit is detected on VTarget (in addition to shutting down VTarget). In this case, the status LED will blink quickly.