Now let's look at how we can reduce the power consumption of the application, and verify that it is improved.
A first thought might be to get rid of the delay loop and run the LED blinker of a timer interrupt. In addition, a simple example like this doesn't need to run at high-speed, so we can use the clock prescaler to run slower. The code below is included in project low_power_102.
#include <avr/io.h> #include <avr/interrupt.h> // Timer 0 ISR ISR (TIMER0_OVF_vect) { if (PORTB == 0x00) { // LED is OFF, turn it on PORTB = (1 << 5); // Shortened timeout for on cycle TCNT0 = 0x102; } else { // LED is ON, turn it off PORTB = 0x00; } } int main(void) { // Change the clock prescaler CLKPR = (1 << CLKPCE); // Scale by DIV64 CLKPR = (1 << CLKPS2) | (1 << CLKPS1) | (0 << CLKPS0); // Port B5 to output DDRB = (1 << 5); // Timer0 DIV 1024 TCCR0B = (1 << CS02) | (1 << CS00); // Overflow interrupt enable TIMSK0 = (1 << TOIE0); // Interrupts on sei(); // Do nothing while (1) ; }
Todo:
- Build the project/solution (F7)
- Program the application into the target device using Start Without Debugging (Ctrl+Alt+F5)
- Switch to Data Visualizer to see the results
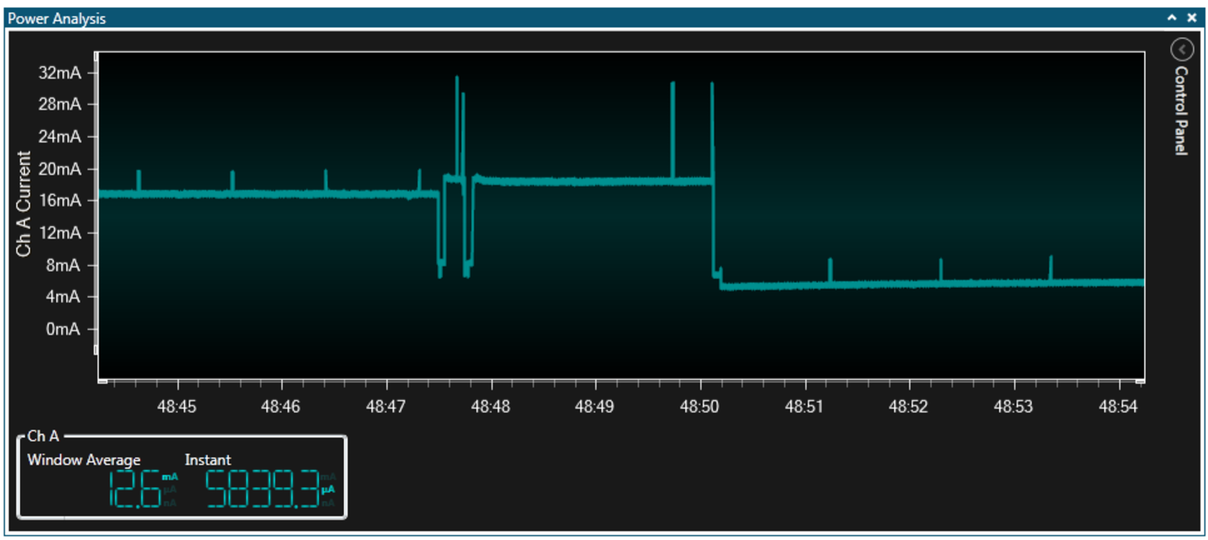
The plot above was captured while reprogramming the target. What can we see
from this plot?
- Two negative power pulses are seen (the device is pulled into reset)
- Four positive pulses are seen (read ID, erase, program flash, and verify flash)
- The new application starts to execute
Leaving the application to run for a few seconds should give you a plot similar to this one:
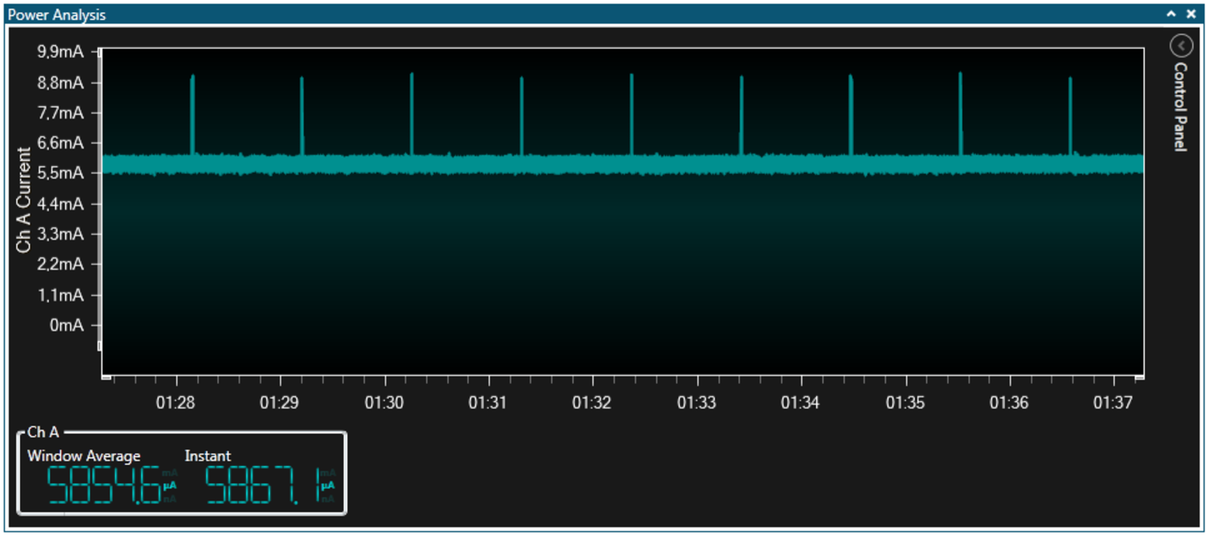
What can we see from this plot?
- The kit now draws about 6mA with the LED OFF
- Current draw increases to about 9mA when the LED is pulsed ON
- The 1% duty cycle still seems approximately correct
Result: Power consumption has been significantly improved
by clocking the device slower.
Important: Because this example prescales the clock to 8MHz/64, the ISP
programming clock must be set to less than 32kHz to be below 1/4 of the main clock
when attempting to reprogram the device!